Free radicals and oxidative stress
Our skin is a living organ in biological processes take place, such as cellular respiration and vitamin D production. Some of these natural reactions generate free radicals, which are molecules, atoms or ions that have at least one unpaired electron. Because of these unpaired electrons, free radicals are highly unstable and reactive.
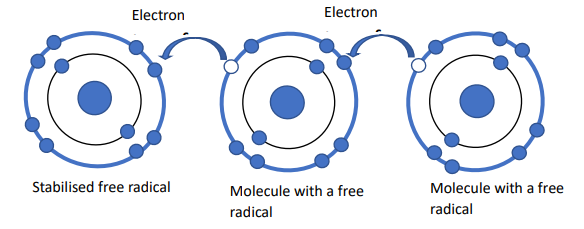
The molecules need to pair from single electrons to become more stable. They are getting electrons from anther molecules and pair up to have stable molecules. This process is called an oxidation reaction. The problem is that now that the second molecule has lost an electron, it becomes a new free radical, thereby creating a chain reaction.
The most important free radicals in our body are called reactive oxygen species (ROS). They interact with lipids, proteins and DNA, and can cause cellular damage in many way. However, some oxidative reactions caused by free radicals are beneficial for our organism; for example, the cell division cycle to regulate and etc.
These reactions with a complex antioxidant system will cause to our body damage. Free radicals are highly unstable molecules which naturally formed when you exercise and when your body converts food into energy. The body can be exposed to free radicals from a variety of environmental sources, such as air pollution, sunlight and smoke. Antioxidants are molecules that fight and neutralise free radicals, stopping the oxidative chain reaction before vital compounds are harmed. They protect the cells from oxidative damage and reduce the impact it causes.
Free radicals are responsible for creating inflammation and prematurely aging and skin. Antioxidants are the opposites of free radicals. They make donating electron to clean up free radicals and prevents it from damaging cells. Antioxidants give a protective effect against aging and disease.
Antioxidants to prevent early signs of ageing
The skin is constantly exposed to external factors, mainly UV radiation: sun damages is a huge aging factor of the skin. Antioxidants may help to protect with using sunscreen, and calm inflammation; which create by nature and antioxidant can help to reduce inflammation and will have smooth skin. Oxidative stress then accelerates the ageing process and causes the formation Electron transfer Electron transfer Stabilised free radical Molecule with a free radical Molecule with a free radical of wrinkles, hyperpigmentation, dryness, and loss of skin tone. The use of cosmetics containing antioxidant actives helps neutralise the formation of free radicals, thereby slowing down the visible signs of ageing.
Some antioxidants used in cosmetics are naturally present in our skin, which is the case of compounds such as vitamin E, vitamin C, and coenzyme Q10, for example. Their topical use helps boost our natural antioxidant protection.
The skin can also benefit from the cosmetic use of some plant extracts that are good sources of natural antioxidant compounds. Plants produce these substances to protect themselves from the sun and other oxidising factors. Recently, interest in plant antioxidants for cosmetic use has grown, with many scientific studies pointing out their benefits. These natural antioxidants can be polyphenols, flavonoids, carotenoids and terpenes, among others.
Plant antioxidants for skin
As we are natural formulators, we are particularly interested in these plant-extracted antioxidants. Fortunately, many natural antioxidants are available in forms easy for us to include in our cosmetic formulations. Below, we list some you might like to explore to include in your formulations.
Green tea
The extract of the Camellia sinensis leaves contains catechins, a class of polyphenols with remarkable antioxidant properties. In fact, one of these catechins, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), is one of the most studied polyphenols. Green tea extracts and EGCG have been shown to reduce the amount of ROS in the skin, diminishing, and even reversing the impact of photoageing and UV damage. Besides that, the topical use of products containing green tea extract can reduce the production of collagen-degrading enzymes in the skin.

Grapes
These fruits are rich in antioxidant compounds. Grape seeds contain proanthocyanidins, which are powerful free radical scavengers. They show more antioxidant activity than vitamin C and E and can even help regenerate these vitamins, presenting synergistic antioxidant activity when combined with them. Grape skin and red wine also contain resveratrol, a polyphenol with strong antioxidant properties. Based on the most recent studies, it is possible to say it helps protect the skin against oxidative damage caused by free radicals and UV radiation.
Rosemary
The leaves of Rosmarinus officinalis are the source of various antioxidant substances. Most of this activity comes from carnosol and carnosic acid, but ursolic, rosmarinic, and caffeic acids take part in these properties as well, working as free radical scavengers. Rosemary essential oil contains monoterpenes such as 1,8-cineol and alpha-pinene that act as antioxidants too.
Pine bark
Maritime pine (Pinus pinaster) bark extract, also known commercially as pycnogenol, is widely studied for its strong antioxidant properties. It contains phenolic compounds such as proanthocyanidins, which are remarkable antioxidants, regenerating and protecting vitamin C and E from oxidation. Also, this extract has some phenolic acids, such as caffeic and ferulic acids, which are potent free radical scavengers. Some studies suggest that this extract can help slow down the appearance of ageing signs, even reducing hyperpigmentation.
Pomegranate
The fruit and rind of Punica granatum are rich in ellagic acid, a polyphenolic compound that enhances the activity of antioxidant enzymes present in our skin. Pomegranate extract also helps reduce hyperpigmentation and protects the skin against UV damage.
By Dr. Aishah Abdullah, Lu Lu Taung Mai
Tarikh Input: 09/09/2022 | Kemaskini: 09/09/2022 | emma
PERKONGSIAN MEDIA