Chemistry is involved in various energy production methods, including fossil fuel combustion, nuclear reactions, and renewable energy technology like solar cells. Understanding chemical reactions and energy transfer processes is necessary for developing efficient and sustainable energy sources.
A solar cell is an electronic device which directly converts sunlight into electricity. Light shining on the solar cell produces both a current and a voltage to generate electric power.
Firstly, it starts with the absorption of photons from sunlight. Photons are packets of energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation. When sunlight hits the solar cell, photons are absorbed by the semiconductor material. Semiconductor material is something that can conduct electricity better than an insulator but not as well as a metal.
The absorbed photons transfer their energy to electrons in the semiconductor material, causing them to become excited and jump from the valence band to the conduction band, leaving behind an electron deficiency known as a hole in the valence band. This process creates electron-hole pairs.
Once the electron-hole pairs are generated, an electric field within the semiconductor material separates the positively charged holes and negatively charged electrons. This separation creates a voltage potential across the solar cell.
The separated electrons and holes are then guided by the electric field. The electrons are collected by metal contacts on the front surface of the solar cell, while the holes are collected by metal contacts on the back surface. This flow of electrons constitutes an electric current.
The electric current generated by the flow of electrons can be used to power electrical devices when the solar cell is connected to an external circuit.
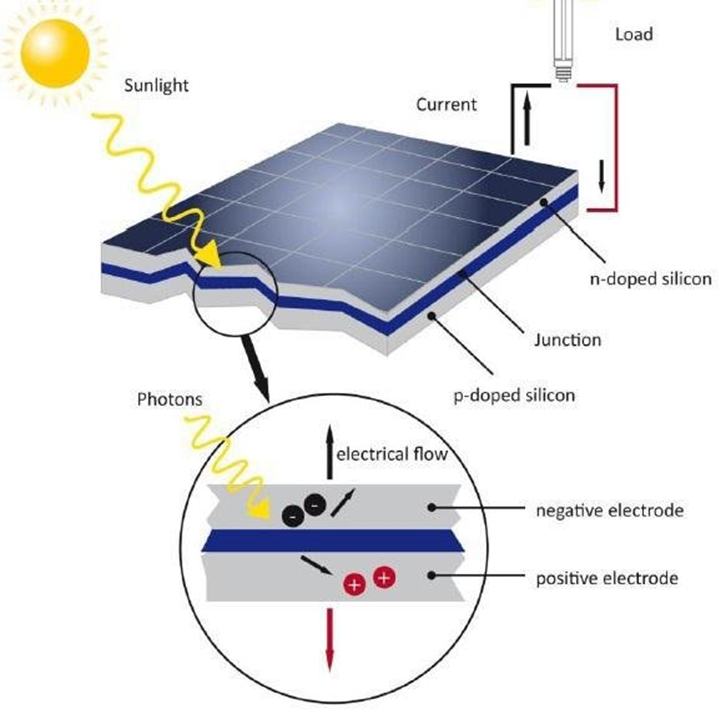
Silicon, Si is the most common semiconductor material used in solar cells and in computer chips. It is also the second most abundant material on Earth. Crystalline silicon cells are made of silicon atoms connected to one another to form a crystal lattice. This lattice provides an organized structure that makes conversion of light into electricity more efficient. It also lows in cost and long lifetime expected to last for 25 years or more.


Noor Hidayu binti Aris
Chemistry Unit, ASPutra
Date of Input: 16/05/2024 | Updated: 16/05/2024 | hasniah
MEDIA SHARING









.jpeg)












