Well, it is predictable to see the increasing number of accidents and fatalities as there are more and more people driving on the road. Therefore, cars are designed with safety elements to protect occupants of the vehicle
and to ensure minimal damage is caused when an accident occurs. In this article, we will express how physics is involved in automobile collisions and how it is used to prevent injuries. Such safety features including seat belt, automatic airbags, crumple zone, and headrest which all will be discussed in depth later below.
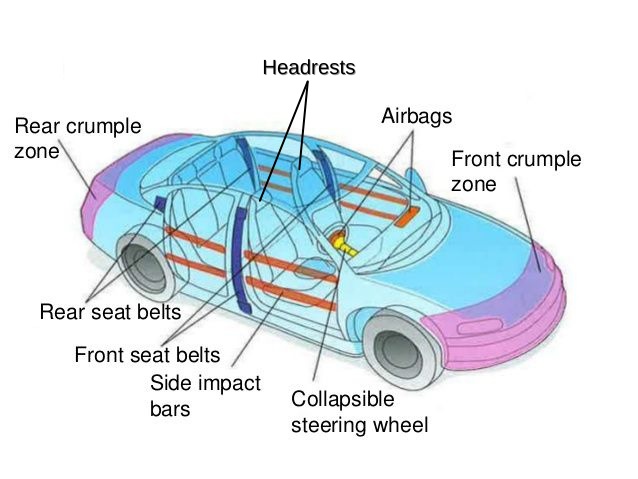
First off, when cars bounce off each other, there is a larger change in momentum which in result a larger impulse. This means that the occupants of the car will experience a greater force. Car manufacturers used this idea to design crumple zones into cars, especially on the front and rear of the car. This way, the cars tend to have a greater chance of crumpling rather than rebounding in a collision. When cars crumple together, there is a smaller change in momentum as it happens over a longer time and therefore a smaller impulse. These effects will increase their chances of survival in accidents.
Next, we will talk about headrests. The headrest can be associated with Newton’s First Law which is inertia. Newton stated that the body that is moving in constant motion or at rest will remain at rest or constant moving
unless there is a force applied. This can be portrayed with a situation, imagine you are driving in a constant motion for 60 km per hour on a highway, suddenly you are being hit by another vehicle that drives for 120 km per hour. When there is sudden force, your body will lurch forward and backward. Therefore, headrest plays a role in preventing you from sustaining whiplash neck injury by limiting the rearward movement. This will reduce the negative impact of inertia from the sudden force towards the seat occupant. Moreover, whenever an accident happens, the automatic airbag system in our car acts as a cushion for the head and body which will prevent injuries to the driver and front passenger. This is because it is an occupant-restraint system for the vehicles that use a bag that inflates and deflates quickly during a collision. It is designed using the impulse, or momentum change principles. When a driver is involved in an accident, their momentum propels them forward, causing them to collide with the steering wheel. By installing an airbag in the vehicle, a smaller impulsive force is applied over a longer period of time to bring the driver's momentum to a halt. Without the airbag, the driver is subjected to a large impulsive force over a short period of time, resulting in increased damage.
Last but not least, seat belts stop you lose from losing balance inside the car if there is a collision. Upon sensing a collision the seat belt lock in place automatically. Hence, when an accident occurs, there is no unbalanced force acting on the person, so they continue to remain in their position. The person moves against the seat belt and the seat belt would exert a force on it as mentioned in Newton’s Third Law. The seat belt then prevents a person from being thrown due to inertia. This can impose a slow down on the person and reduce injury. We can conclude that physics can benefit us and prevent us from dangers while driving a car or riding a motorcycle. Use and apply this concept to keep us from accidents in our daily life.
Ariff Ameer Aizad Bin Nordin, Keerthana Shri A/P Kalai Vanan, Afiqah Hasfarliatasha Binti Abdul Halim,
Aishah Humaira’ Binti Ahmad Azam, Emma Ziezie
Date of Input: 29/06/2022 | Updated: 01/02/2025 | emma
MEDIA SHARING